Khan Academy on a Stick
Executive systems of the brain
Aristotle asserted that what separates humankind from non-human animals is our ability to engage in high reasoning. This reasoning includes solving problems, making decisions, recalling and recording memories, and expressing complex emotions. We’ll explore different states of consciousness, and how our brain adapts and responds to stimuli. Learn all about the higher-order executive functions of the brain, which help you remember your friend’s name, learn a new language, and even fall asleep at night.
-
 Piaget's stages of cognitive development
Piaget's stages of cognitive development
Learn about the stages and developmental milestones in Piaget's theory of cognitive development.
-
 Problem solving
Problem solving
Learn about types of problems and common approaches to solving them.
-
 Decision making
Decision making
Learn about common heuristics, biases, and other factors that affect our decisions.
-
 Semantic networks and spreading activation
Semantic networks and spreading activation
Learn about how knowledge is organized in the mind.
-
 Intelligence
Intelligence
Learn about different definitions of intelligence and the nature/nurture debate in the context of intelligence.
-
 Aging and cognitive abilities
Aging and cognitive abilities
Learn about how cognitive abilities change as we age.
Cognition
Explore cognitive development and intelligence, as well as how our minds solve problems, make decisions, and represent knowledge.
-
 Divided attention, selective attention, inattentional blindness, & change blindness
Divided attention, selective attention, inattentional blindness, & change blindness
Learn about divided attention, selective attention, inattentional blindness, & change blindness. By Carole Yue.
-
 Theories of selective attention
Theories of selective attention
Learn about the three major theories of selective attention. By Carole Yue.
-
 Theories of language and cognition
Theories of language and cognition
Learn about theories of the relationship between language and cognition. By Carole Yue.
-
 Theories of language development: Nativist, learning, interactionist
Theories of language development: Nativist, learning, interactionist
Learn about the nativist, learning, and interactionist theories of human language development. By Carole Yue.
-
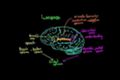 Language and the brain: Aphasia and split-brain patients
Language and the brain: Aphasia and split-brain patients
Learn about language areas of the brain and the effects of damage to those parts of the brain. By Carole Yue.
Attention and language
Have you ever tried to multi-task? Explore the concept of selective and divided attention, as well as the role of language in cognition and development.
Sleep and consciousness
Explore states of consciousness, circadian rhythms, sleep stages, and sleep disorders.
-
 Information processing model: Sensory, working, and long term memory
Information processing model: Sensory, working, and long term memory
Learn about the information processing model of human memory.
-
 Encoding strategies
Encoding strategies
Learn about rote rehearsal, chunking, mnemonic devices, self-referencing, and spacing.
-
 Retrieval cues
Retrieval cues
Learn about how priming, environmental context, and internal state affect memory.
-
 Retrieval: Free recall, cued recall, and recognition
Retrieval: Free recall, cued recall, and recognition
Learn about three types of retrieval: free recall, cued recall, and recognition.
-
 Memory reconstruction, source monitoring, and emotional memories
Memory reconstruction, source monitoring, and emotional memories
Learn about memory reconstruction, source monitoring, and flashbulb memories.
-
 Long term potentiation and synaptic plasticity
Long term potentiation and synaptic plasticity
Learn about synaptic plasticity and long-term potentiation, the physiological mechanism behind learning.
-
 Decay and interference
Decay and interference
Learn about decay and interference in human memory.
-
 Aging and cognitive abilities
Aging and cognitive abilities
Learn about how cognitive abilities change as we age.
-
 Alzheimer's disease and Korsakoff's syndrome
Alzheimer's disease and Korsakoff's syndrome
Learn about how Alzheimer's Disease and Korsakoff's Syndrome affect memory.
Memory
Explore the structure of human memory; processes involved in normal encoding, retrieval, forgetting, and aging; and diseases affecting memory.

 States of consciousness
States of consciousness Sleep stages and circadian rhythms
Sleep stages and circadian rhythms Dreaming
Dreaming Sleep disorders
Sleep disorders Hypnosis and meditation
Hypnosis and meditation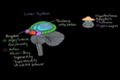 Emotions: limbic system
Emotions: limbic system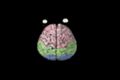 Emotions: cerebral hemispheres and prefrontal cortex
Emotions: cerebral hemispheres and prefrontal cortex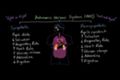 Autonomic nervous system (ANS) and physiologic markers of emotion
Autonomic nervous system (ANS) and physiologic markers of emotion Three components of emotion and the universal emotions
Three components of emotion and the universal emotions Theories of Emotion
Theories of Emotion